Optimizing the Process of Baking Wedding Sweets
Name: Optimizing the process of baking wedding sweets
Author: Michaela Červinková (cerm18) (talk) 15:19, 21 January 2022 (CET)
Method: Discrete simulation
Tool: SIMPROCESS
Contents
Problem definition
There is a wedding tradition in Czech Republic of baking wedding sweets and then handing them out to the guests of the weeding as a form of invitation. Process of baking usually takes whole day and several helpers in the kitchen are needed. Into paper baskets are usually packaged two types of sweets: several small ones with 3 different flavors and one so-called "rohový koláč". Which are then delivered by the bride to wedding guests. For the purpose of this simulation are process and needed ingredients simplified.
The goal is to optimize the number of helpers in the kitchen and find optimal amount of basic ingredients for specified number of guests.
Method
As a method for simulation of baking goods was chosen method named discrete-event simulation, which is characterized as simulation that generates a sequence of events that than trigger changes in the model. This method is suitable for dynamic queuing models that can be different business processes like serving customers, manufacture of goods, handling incidents, etc.
For this kind of simulation was chosen software tool SIMPROCESS as it is one of the tools for dynamic queuing simulations. SIMPROCESS provides for its users functions like Process Mapping, Event-driven Simulation and Activity-based Costing in user-friendly graphical interface so it is easy to learn. In this course was used trial version of this software University Edition. In general this dynamic modelling tool is used for simulating flow of entities through defined process which is represented by connected activities that require certain resources. Flow of such entities is measured and different results can be compared.
Model
Created model simulates day of baking wedding sweets, precisely 8 hours. Bride has available for baking number of cooks, 2 ovens and 3 baking trays. There is limitation of lunch break when process must be stopped and all pastry cooks stop working. Goal is to find optimal number of cooks and amount of ingredients for 120 guests. Given the fact that baskets full of sweets are given to households instead of individual guests,120 guests is divided by approximately 4 household members, which is 30 paper baskets that need to be assembled.
This model consists of several entities and resources listed below.
Entities
- Order for paper basket
- Big sweet
- Tray with big sweets
- Small sweet
- Tray with small sweets
- Filled paper basket
Resources
| Resource Name | Units | Consumable |
|---|---|---|
| Pastry cook | 9 | No |
| Oven | 2 | No |
| Baking Tray | 3 | No |
| Sugar for coating (bowl) | 2 | No |
| Flour (g) | 4800 | Yes |
| Sugar (g) | 1000 | Yes |
| Curd (g) | 1000 | Yes |
| Plum jam (g) | 1000 | Yes |
| Poppy seed filling (g) | 1000 | Yes |
| Paper basket (g) | 30 | Yes |
Lunch break for resource Pastry cook as mentioned above is defined in the simulation using Resource Downtime and timeframe is from 12:00 am till 13:00 am.
Higher Level Model
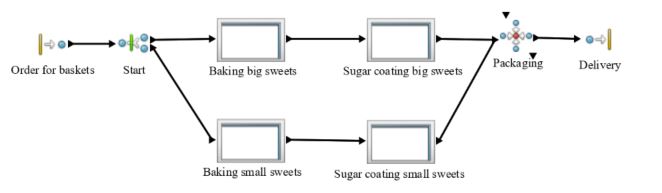
Higher level of the model as visible in the picture below consist of 4 activities and 4 processes which then have each different activities inside.
The beginning of whole process starts with Order for paper baskets represented by activity Generate. This activity is set to generate 30 entities of Order for paper basket a day to be able to request specified amount of baskets for defined number of guests.
Then these entities are duplicated in activity named Start which is representing cloning of the entities to work with same amount of orders in both following branches. Model has two branches, because different processes are needed for small type of sweets and different for bigger ones.
After processes and their activities in these two branches are completed, entities of small and big sweets go to activity Packaging were are assembled using activity Assemble into individual paper baskets. The proportions are 25 small sweets and 1 big sweet into one paper basket. This activity requires two different resources which is one pastry cook and one paper basket for each assembled entity which is Filled paper basket. Duration of assembling activity of one basket is 5 minutes so value exp (5.0) was set.
Then as finishing part of this model entities Filled paper baskets are delivered in activity Delivery represented by dispose activity.
Lower Level Model
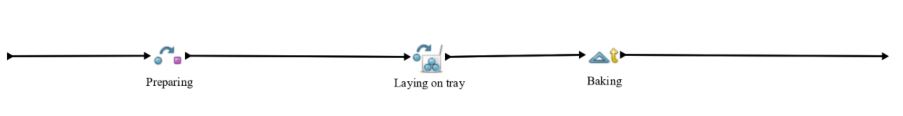
Baking big sweets
Process of baking big sweets consists of three different activities. Preparing using transform activity, Laying on the tray using batch activity and Baking using delay activity.
At first entity Order for paper basket is transformed during transform activity named Preparing. Because it is known that in each basket goes only one big sweet, entity Order for paper basket is in this case being transformed into one big sweet that is being created. For the purposes of this simulation was duration of the activity set to exp (90.0) seconds, as preparation of 30 big sweets would take 45 minutes. This activity requires several resources listed below.
| Resource Name | Units |
|---|---|
| Pastry cook | 2 |
| Flour (g) | 20 |
| Sugar (g) | 5 |
| Curd (g) | 4 |
| Plum jam (g) | 4 |
| Poppy seed filling (g) | 4 |
Then transformed entities are batched which is representing the activity of laying prepared sweets on the baking tray. Big sweets are batched by 15 pieces as that is number of big sweets that can fit to the baking sheet of standard size. This activity takes exp (5.0) minutes and used resources are one pastry cook and one baking tray.
After entities are batched, batched entity Tray with big sweets is going to delay activity portraying baking in the oven. The duration of baking is set to exp (30.0) minutes and it needs one oven and one pastry cook as required resources.
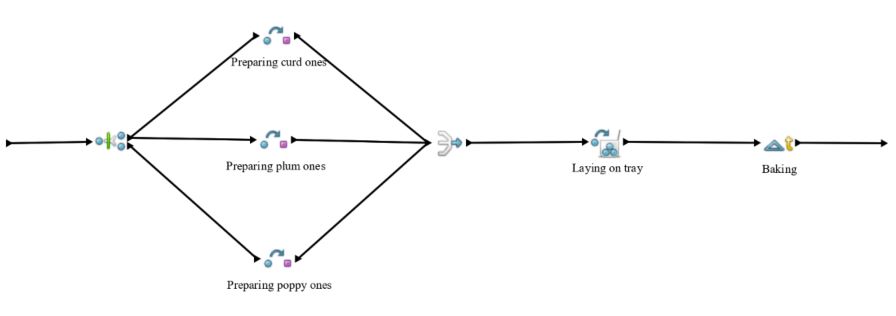
Baking small sweets
Similarly to process of baking big sweets works also this process with difference that before activity of laying sweets on the baking tray and activity of baking must be original entity Order for paper basket cloned again so that appropriate amounts of different kinds of sweets can be made during activities representing preparing.
Each preparing activity for which was used again transform tool creates 9 small sweets of different kinds and takes exp (10.0) minutes. Below are specified required resources and their needed amounts.
| Resource Name | Preparing Curd Ones | Preparing Plum Ones | Preparing Poppy Ones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pastry cook | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Flour (g) | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| Sugar (g) | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| Curd (g) | 23 | - | - |
| Plum jam (g) | - | 23 | - |
| Poppy seed filling (g) | - | - | 23 |
Outputs from these activities are then merged together and batched similarly as in previous process. Because of their size they can be batched by 56 pieces into one tray of small sweets. As this is quite big amount of sweets, duration of this activity is set to exp (10.0) minutes. And again one baking tray and one pastry cook is needed.
Batched entity then continues to delay activity representing baking which is set to have duration exp (25.0) minutes requiring one pastry cook and one oven as resources.
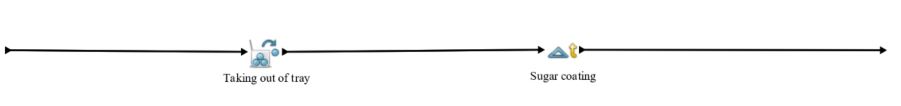
Sugar Coating
After both of previous processes of baking sweets is process of sugar coating created sweets consisting of two activities. Difference between them is in the duration of activities.
Activity Taking out of tray is implemented by using tool unbatch which converts entities of sweets from their batch form to individual ones. This activity takes in both cases exp (10.0) minutes. For this activity only pastry cook and baking tray is needed.
After that follows activity of sugar coating which takes in one case exp (30.0) seconds and in the other case exp (45.0) seconds. From resources pastry cook and bowl with sugar is needed. Sugar-coated entities of sweets then follow defined process as shown in higher level model.
Results
Model generated following results. We can see from them that in optimized result all orders were fulfilled. And only 60 small sweets remained in the system after time was up. Total Generated number of Order of Paper Basket is so high because it was cloned four times which corresponds to 30 x 4 being 120.
| Entity Names | Total Generated | Remaining In System | Total Processed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Sweet | 30 | 0 | 30 |
| Filled Paper Basket | 30 | 0 | 30 |
| Order for Paper Basket | 120 | 0 | 120 |
| Small Sweet | 810 | 60 | 750 |
| Tray with Big Sweets | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Tray with Small Sweets | 14 | 0 | 14 |
Simulation was finetuned to provide as good results as possible by adjusting number of pastry cooks and amount of resources. Less than 9 pastry cooks was not sufficient to get in on time if we take in consideration also downtime in form of lunch break. When was simulation runed without the downtime less cooks could get it all done. And also at the same time more than 9 pastry cooks were redundant.
| Entity Names | Total in System | Processing | Wait for Resources | Hold for Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big Sweet | 242.4 | 60.9 | 126.5 | 55 |
| Filled Paper Basket | 5.6 | 4.9 | 0.7 | 0 |
| Order for Paper Basket | 57.4 | 7.1 | 50.3 | 0 |
| Small Sweet | 304.0 | 38.1 | 238.2 | 27.7 |
| Tray with Big Sweets | 123.4 | 60.3 | 63.2 | 0 |
| Tray with Small Sweets | 197.6 | 38.2 | 159.4 | 0 |
| Resource Names | Defined Capacity | Capacity | Idle: Average | Idle: Max | Busy: Average | Busy: Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curd (g) | 1000 | 320.1 | 302.8 | 1000 | 17.3 | 207 |
| Flour (g) | 4800 | 637.8 | 555.5 | 4800 | 82.2 | 405 |
| Paper basket | 30 | 21.8 | 21.5 | 30 | 0.3 | 5 |
| Plum jam (g) | 1000 | 273.3 | 260.6 | 1000 | 12.7 | 184 |
| Poppy seed filling (g) | 1000 | 237.2 | 224.9 | 1000 | 12.3 | 207 |
| Sugar (g) | 1000 | 143.9 | 127.3 | 1000 | 16.6 | 81 |
From results displaying percent utilization by state for non-consumable resources, can be seen 12.5 % in planned which is cause by the application of downtime for this resource. Otherwise we can see that ovens are busy almost half of the time which is not the case of the baking trays, which is caused by not including baking tray as a resource during baking activity.
| Resource Names | Idle | Busy | Planned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pastry cook | 33.8 % | 53.7 % | 12.5 % |
| Oven | 55.9 % | 44.1 % | 0.0 % |
| Baking Tray | 81.2 % | 18.8 % | 0.0 % |
| Sugar for coating (bowl) | 24.4 % | 75.6 % | 0.0 % |
Conclusion
Overall goal of the simulation was fulfilled, optimal number of pastry cooks has been found and approximate numbers of ingredients have been determined. Even though this model was created with baking specific sweets in mind, with some adjustments it could be used even for small bakery where application of initial activity of generating orders could be more meaningful.
Citations
https://megvkuchyni.cz/recepty/speciality/svatebni-special-jak-na-svatebni-kolacky/
https://www.svetsvateb.cz/2021/02/623262-svatebni-kolacky/
+ experience