Difference between revisions of "Profit in store vs e-shop"
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
--- | --- | ||
| − | In the graphs below we can see the revenue of the e-shop and store apart in more detail. On the graphs can be seen how e-shop revenue is influenced by | + | In the graphs below we can see the revenue of the e-shop and store apart in more detail. On the graphs can be seen how e-shop revenue is influenced by advertisement. |
Latest revision as of 00:01, 26 January 2023
Problem definition
An unnamed company that sells carpets has its own store in Prague. During COVID-19 the company reopened an e-shop, so it currently has two mutually supporting sales channels. Both types of stores have their advantages and disadvantages. At the same time, there are various factors that affect the profit. Examples of these factors are the following: customer satisfaction and needs (carpet quality, order processing speed, price, etc.), expenses (advertising, rent, employees, etc.), the possibility of expansion, etc. To ensure customer satisfaction the company should make some expenses.
The goal of this simulation is to find out what parameters can increase profit the most (individually for each type of store), to find a balance between expenses to satisfy the customers in order to achieve the profit, and in the end to compare these parameters.
Method
The Vensim program is used as a modeling tool, which makes it possible to display and simulate the dynamics of the entire system.
Variables
Profit
the amount of money a business makes after all of its expenses have been paid.
= revenue - cost Units: CZK
Cost
the amount of money that is required to acquire a product or to raise customers' satisfaction.
= fixed cost e-shop + fixed cost store + variable cost e-shop + variable cost store Units: CZK
Revenue
the amount of money a business earns from its sales.
= revenue e-shop + revenue store Units: CZK
Fixed cost e-shop
costs that do not change with the level of sales for an e-commerce business.
= salary * employments e-shop + 1000 Units: CZK
Fixed cost store
costs that do not change with the level of sales for a physical store.
= salary * employments store + building rent Units: CZK
Variable cost e-shop
costs that vary with the level of sales for an e-shop.
= 5000 + advertising budget + gifts + (money paid for discount/2) Units: CZK
Variable cost store
costs that vary with the level of sales for a physical store
= 10000 + gifts + (money paid for discount/2) Units: CZK
Advertising budget
the amount of money allocated by a business for promoting its products. The company is advertising through Google Ads and pays for each click.
= RANDOM UNIFORM(20, 1000 , 50 )*15 Units: CZK
Building rent
the cost of renting a physical location for a business.
= 80000 + parking Units: CZK
Salary
the amount of money that is paid to an employee for their work.
= 25000 * opening hours Units: CZK
Employments store
the number of employees working in a physical store. = 4
Employments e-shop
he number of employees working in an e-shop.
= 1
Opening hours
the time when a business is open. If there is a holiday the store is open and employees will get a +25% to their salary.
= IF THEN ELSE(holiday=1, 1.25 , 1 )
Holiday
= RANDOM UNIFORM(0, 1, 1)
Parking
the availability of parking for customers at a physical location.
= 5000 Units: CZK
Revenue e-shop
the amount of money earned from an e-shop. The company's revenue always increases by 20% spent on advertisements.
= price * quantity sold e-shop * customer satisfaction e-shop + (advertising budget*0.2) Units: CZK
Revenue store
the amount of money earned from a physical store.
= price * quantity sold store * customer satisfaction store Units: CZK
Quantity sold e-shop
the number of products sold by e-shop.
= RANDOM UNIFORM(500, 1000 , 800) Units: m^3
Quantity sold store
the number of products sold by a physical store.
= RANDOM UNIFORM(300, 700, 500 ) Units: m^3
Price
the amount of money that is charged for a carpet
= RANDOM UNIFORM(150, 650 , 300)+delivery Units: CZK
Delivery
the delivery cost depends on the order weight. If the order cost is more, than 5000 CZK then the delivery is free.
= IF THEN ELSE(order cost>5000, 0 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight<5, 159 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>5 :AND: order weight<15, 289 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>15 :AND: order weight<30, 399 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>30 :AND: order weight<50, 599 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>50 :AND: order weight<75, 799 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>75 :AND: order weight<100, 999 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>100 :AND: order weight<150, 1389 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>150 :AND: order weight<300, 1649 , IF THEN ELSE(order weight>300 :AND: order weight<400, 1749 , 1979 ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) Units: CZK
Order weight
the weight of an order placed by a customer.
= RANDOM UNIFORM(1, 500, 1) Units: kg
Order cost
the cost of processing and fulfilling an order placed by a customer.
= RANDOM NORMAL(200, 100000 , 5000 , 2000, 1000) Units: CZK
Gifts
items that are given to customers as part of a promotion. If the order cost is bigger than 2000, customers will get a gift, which cost 500 CZK.
= IF THEN ELSE(order cost>2000, 500, 0 ) Units: CZK
Discount
a reduction in the regular price of a product. The current discount is 10 %
= RANDOM UNIFORM(0.6, 0.9 , 0.7) Units: %
Money paid for discount
the money which the company spent to give the customer a discount
= order cost*discount Units: CZK
Customer satisfaction
the degree to which customers are happy with a business's products.
= customer satisfaction grow
Customer satisfaction grow
the increase in customer satisfaction over time.
= customer satisfaction e-shop + customer satisfaction store
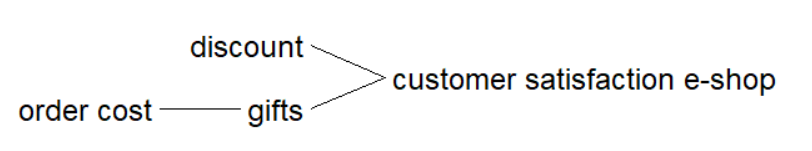
Customer satisfaction e-shop
the degree to which customers are happy with e-shop's products.
If the store gives gifts, it will increase revenue by 2%. If the store gives a discount of 30%, it will increase revenue by 20%. If the store gives a discount of 10-20%, it will increase revenue by 10%.
If the store has gifts and a 10-20% discount, the revenue will increase by 12%. If the store has gifts and a 30% discount, the revenue will increase by 22%.
= IF THEN ELSE( (IF THEN ELSE(gifts=500, 1.02 , 1 ) + IF THEN ELSE(discount<0.7, 1 , IF THEN ELSE(discount>0.7 :AND: discount<0.8, 1.2 , 1.1 ) ) )= 1.12 , 1.12 , 1.22) Units: %
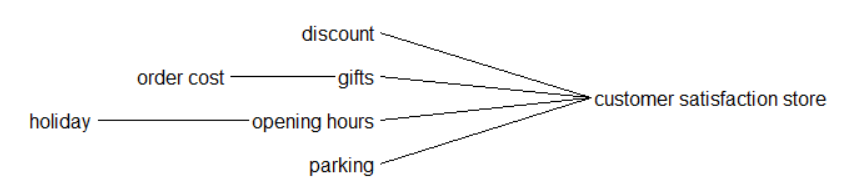
Customer satisfaction store
the degree to which customers are happy with a physical store's products.
If the store has an available parking spot, it will increase revenue by 2%. If the store gives gifts, it will increase revenue by 2%. If the store gives a discount of 30%, it will increase revenue by 20%. If the store gives a discount of 10-20%, it will increase revenue by 10%. If the store works on holidays, it will increase revenue by 5%.
If the store has gifts, parking, working on holidays, and a 10-20% discount, the revenue will increase by 19%. If the store has gifts, parking, working on holidays, and a 30% discount, the revenue will increase by 29%.
= IF THEN ELSE( (IF THEN ELSE(parking=5000, 1.02 , 1 ) + IF THEN ELSE(opening hours=1.25, 1.05 , 1 ) + IF THEN ELSE(gifts=500, 1.02 , 1 ) + IF THEN ELSE(discount<0.7, 1 , IF THEN ELSE(discount>0.7 :AND: discount<0.8, 1.2 , 1.1 ) ) )= 1.19 , 1.19 , 1.29) Units: %
Model
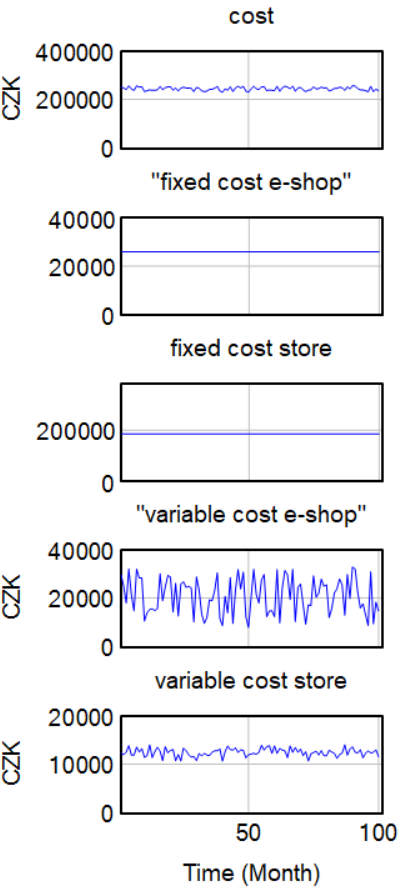
The model represents a company and its revenue and costs separated into different variables to represent different sales channels (e-shop and store). As can be seen in the model fixed costs for the e-shop and store do not differ that much. Variable cost does not differ that much either, except for the advertisement budget, which influences e-shop variable cost a lot. On the other hand, revenue is influenced by more variables. Besides typical variables such as the price of the product and sold quantity, it is also influenced by customers' satisfaction. Customers' satisfaction influences the revenue for both e-shop and store.
Results
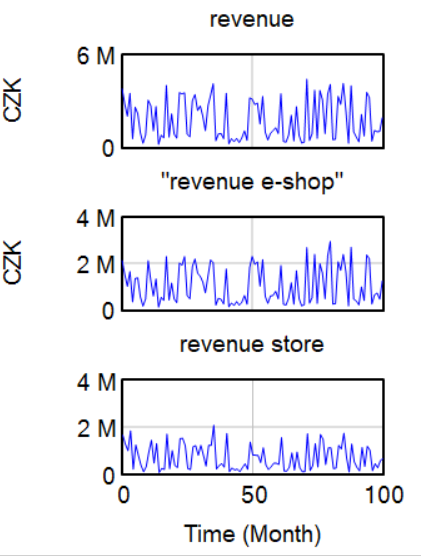
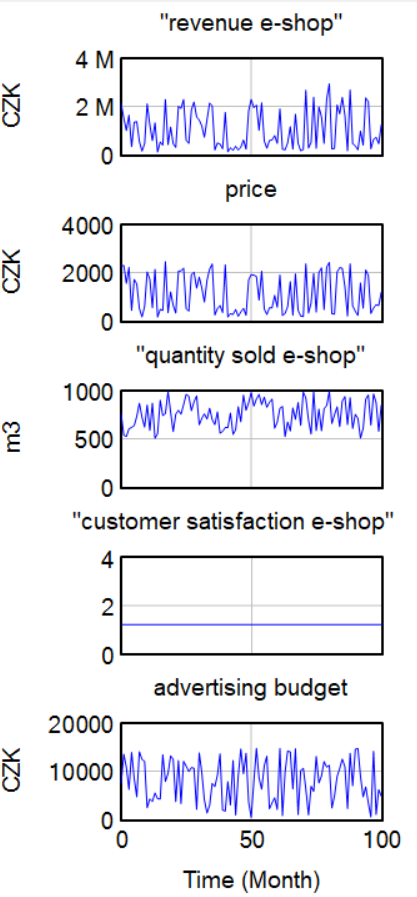
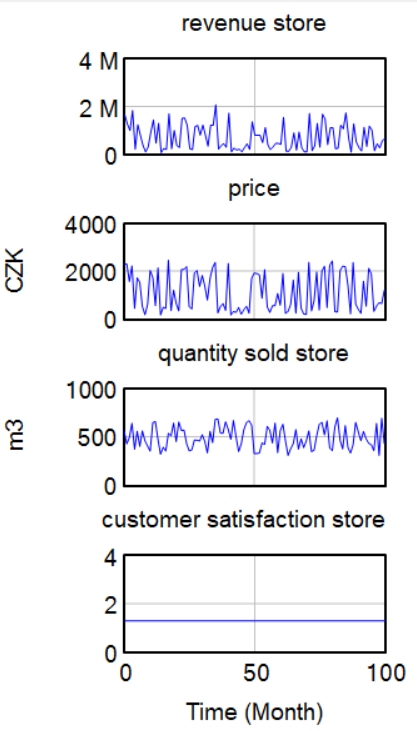
According to the graphs below we can see, that e-shop revenue is much higher than the store's revenue. E-shop revenue is influenced by higher variable costs as the company is spending money on advertising, which makes clients buy more through e-shop.
---
In the graphs below we can see the revenue of the e-shop and store apart in more detail. On the graphs can be seen how e-shop revenue is influenced by advertisement.
---
Even though e-shop revenue is much higher, we can see that customers should be more satisfied with the store as there are more 'perks' in the store.
Conclusion
The final model is not ideal. It is hard to find all variables, that influence company's profit, especially if we are taking into account customers' satisfaction. The simulation does not count some important variables such as the costs that the company needs to spend to buy new carpets, for example. According to the model we can say, that the profit is better at e-shop, even though customer satisfaction is higher at the store. The reason for that is probably advertisement which is increasing the sales on e-shop.