Difference between revisions of "Game theory"
(→Normal form game) |
(→References) |
||
| (374 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" align=right width="200" | ||
| + | ! scope="col" width="30px" |Theory of Games and Economic Behavior | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:TGEB.jpg|thumb|center|200 px|Theory of Games and Economic Behavior]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Theory of Games and Economic Behavior, published in 1944 by Princeton University Press, is a book by mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern which is considered the groundbreaking text that created the interdisciplinary research field of game theory. In the introduction of its 60th anniversary commemorative edition from the Princeton University Press, the book is described as "the classic work upon which modern-day game theory is based." | ||
| + | |||
| + | The book is based on prior research by von Neumann, published in 1928 under the German title "Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele" ("On the Theory of Parlor Games"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The derivation of expected utility from its axioms appeared in an appendix to the Second Edition (1947). Von Neumann and Morgenstern used objective probabilities, supposing that all the agents had the same probability distribution, as a convenience. However, von Neumann and Morgenstern mentioned that a theory of subjective probability could be provided, and this task was completed by Johann Pfanzagl in 1967.<ref>Theory of Games and Economic Behavior. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-, 2014 [cit. 2015-01-22]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory_of_Games_and_Economic_Behavior</ref> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
*'''The Essay topic''': Game Theory | *'''The Essay topic''': Game Theory | ||
*'''Class''':[http://isis.vse.cz/katalog/syllabus.pl?predmet=95726;zpet=..%2Fpracoviste%2Fpredmety.pl%3Fid%3D64%2Clang%3Dcz;jazyk=1;lang=sk 4IT496 Simulation of Systems] (WS 2014/2015) <ref>ŠALAMON, Tomáš. Design of agent-based models: developing computer simulations for a better understanding of social processes. Řepín-Živonín: Tomáš Bruckner, 2011. ISBN 978-809-0466-111. </ref> | *'''Class''':[http://isis.vse.cz/katalog/syllabus.pl?predmet=95726;zpet=..%2Fpracoviste%2Fpredmety.pl%3Fid%3D64%2Clang%3Dcz;jazyk=1;lang=sk 4IT496 Simulation of Systems] (WS 2014/2015) <ref>ŠALAMON, Tomáš. Design of agent-based models: developing computer simulations for a better understanding of social processes. Řepín-Živonín: Tomáš Bruckner, 2011. ISBN 978-809-0466-111. </ref> | ||
| Line 4: | Line 16: | ||
| − | The beginning of | + | The beginning of mathematical game theory originated in 1944, when the book called '''Theory of Games and Economic Behavior''' <ref> COPELAND, A. H. (1945). "Review: Theory of Games and Economic Behavior by John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern". Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 51 (07): 498–504. doi:10.1090/s0002-9904-1945-08391-8.</ref> by mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern was written and published by Princeton University Press. Game theory is the discipline of applied mathematics, that analyzes the spectrum of conflict decision situations that may occur, wherever there is a conflict of interests. |
| − | Game theory models try to analyze these conflict situations and by building a mathematical model of the conflict and computing are trying to find the best strategies for specific parties of the conflict | + | Game theory models try to analyze these conflict situations and by building a mathematical model of the conflict and computing are trying to find the best strategies for specific parties of the conflict.<ref>Teorie her. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2014 [cit. 2015-01-25]. Dostupné z: http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teorie_her</ref> |
Game theory is a branch of, originally, applied mathematics, used mostly in economics and political science, a little bit in biology, that gives us a mathematical taxonomy of social life and it predicts what people are likely to do and believe others will do in cases where everyone's actions affect everyone else. That's a lot of things: competition, cooperation, bargaining, games like hide-and-seek, and poker.<ref>CAMERER, C. (January 2013). TEDX. Acquired in January 2014, z <http://www.ted.com/talks/colin_camerer_neuroscience_game_theory_monkeys?language=en/> </ref> | Game theory is a branch of, originally, applied mathematics, used mostly in economics and political science, a little bit in biology, that gives us a mathematical taxonomy of social life and it predicts what people are likely to do and believe others will do in cases where everyone's actions affect everyone else. That's a lot of things: competition, cooperation, bargaining, games like hide-and-seek, and poker.<ref>CAMERER, C. (January 2013). TEDX. Acquired in January 2014, z <http://www.ted.com/talks/colin_camerer_neuroscience_game_theory_monkeys?language=en/> </ref> | ||
| − | + | = Basic concepts = | |
| − | The basis of most mathematical models of | + | The basis of most mathematical models of game theory is the '''assumption of rationality'''. Every player acts such that he maximizes their profit (their win). |
* The player based on stable preferences sets objectives and strategies to elect the most efficient possible to achieve these objectives. | * The player based on stable preferences sets objectives and strategies to elect the most efficient possible to achieve these objectives. | ||
* The player is confronted by a number of situations and he is able to sort them according to their preferences from the most advantageous to the least advantageous. | * The player is confronted by a number of situations and he is able to sort them according to their preferences from the most advantageous to the least advantageous. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 28: | ||
The assumption of rationality (of each player) is the factor which distinguishes the game theory from the theory of decision. | The assumption of rationality (of each player) is the factor which distinguishes the game theory from the theory of decision. | ||
| − | This alignment must be complete, | + | This alignment must be complete, i. e. must cover all situations and transitive, i. e. if a player prefer the situation A before the situation B and situation C, and must prefer the situation A before the situation C. Based on the preferences of the situation is derived utility function of player. The sole objective of the player is then maximizes the value of the utility function. <ref name="PELIŠ">[PELIŠ, Michal: Teorie her jako formální teorie racionálního rozhodování (Game theory as a formal theory of rational decision-making); In: Soudobá sociologie II (Teorie sociálního jednání a sociální struktury). 1 vyd. 2008, Praha: Karolinum; s. 255-276. ISBN 978-80-246-1413-7. ]</ref> |
| − | + | =Games= | |
| − | |||
All the games that we are considering in this chapter have certain things in common and these are: | All the games that we are considering in this chapter have certain things in common and these are: | ||
| − | * There is a finite set of players assumed (who may be people, groups of people holding the same opinion, or more abstract entities like computer programs or “nature” or “the house”). The least possible number of players is 2. | + | |
| − | * Number of applied strategies may be finite and infinite. For endless strategy plays a role timing of moves. (for game theory consider games with a finite number of strategies) | + | =Games types= |
| − | * Winning types are divided into games with constant sum and games with non-constant sum. | + | |
| − | * | + | * There is a '''finite set of players''' assumed (who may be people, groups of people holding the same opinion, or more abstract entities like computer programs or “nature” or “the house”). The least possible number of players is 2. |
| + | |||
| + | * '''Number of applied strategies''' may be finite and infinite. For endless strategy plays a role timing of moves. (for game theory consider games with a finite number of strategies) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Winning types are divided into games with '''constant sum''' and games with '''non-constant sum'''. | ||
| + | ** In '''constant sum''' games, the strategy for each option is the sum of payroll functions (winnings) of all players '''constant''' - special case of these games are zero-sum games, in which what one player wins, the other player must lose (e. g. chess, tic-tac-toe, popular Chinese game go) | ||
| + | ** In '''non-zero sum''' games, winning the one player might not necessarily mean losing for another player (e. g. prisoner's dilemma, battle of the buddies, politics) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The game ends after a finite number of moves. | ||
| + | ** '''Strategic games''' assumes, that, players will make a one move or decision in the same time (e. g. rock-paper-scissors, prisoner's dilemma) | ||
| + | ** '''Tensile games''' are based on sequences of moves at which the players take turns (e. g. chess, tic-tac-toe) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * According to available information, there are: | ||
| + | ** Games with '''complete information''', each player has complete knowledge of the rules of the game (e. g. chess) | ||
| + | ** Games with '''incomplete information''' occur very rarely in real life(e. g. poker, prisoner's dilemma, Bayesian game). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Players cooperation | ||
| + | ** In '''cooperative games''', players can eventually build coalitions among themselves or negotiate | ||
| + | ** In '''non-cooperative games''' is not possible to create a coalition or negotiate | ||
| + | |||
* At different points in the game, each player has a range of choices or moves. This set of choices is finite. | * At different points in the game, each player has a range of choices or moves. This set of choices is finite. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * After the game ends, each player receives a numerical payoff. This number may be negative, in which case it is interpreted as a loss of the absolute value of the number. For example, in a game like chess the payoff for winning might be +1, for losing -1, and for a draw 0. | + | * After the game ends, each player receives a numerical payoff. This number may be negative, in which case it is interpreted as a loss of the absolute value of the number. For example, in a game like chess the payoff for winning might be +1, for losing -1, and for a draw 0.<ref name="MORRIS">[MORRIS, Peter. Introduction to game theory. New York: Springer-Verlag, c1994, xvi, 230 p. ISBN 03-879-4284-X.]</ref> |
In addition, the following are properties which a game may or may not have: | In addition, the following are properties which a game may or may not have: | ||
* There may be chance moves. In a card game, the dealing of the hands is such a chance move. In chess there are no chance moves. | * There may be chance moves. In a card game, the dealing of the hands is such a chance move. In chess there are no chance moves. | ||
| − | * In some games, each player knows, at every point in the game the entire previous history of the game. This is true of tic-tac-toe and backgammon but not of bridge (because the cards dealt to the other players are hidden). A game with this property is said to be of perfect information. Note that a game of perfect information may have chance moves. Backgammon is an example of this because a die is rolled at points in the game. | + | * In some games, each player knows, at every point in the game the entire previous history of the game. This is true of tic-tac-toe and backgammon but not of bridge (because the cards dealt to the other players are hidden). A game with this property is said to be of perfect information. Note that a game of perfect information may have chance moves. Backgammon is an example of this because a die is rolled at points in the game.<ref name="PELIŠ"/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == Normal form | + | ==[[Normal form]] games== |
Game in the normal form is defined by set | Game in the normal form is defined by set | ||
<math>\{ Q, X_1, ..., X_n, u_1 (x_1,...X_n),..., u_n (x_1,..., x_n) \}</math> | <math>\{ Q, X_1, ..., X_n, u_1 (x_1,...X_n),..., u_n (x_1,..., x_n) \}</math> | ||
| − | where <math>Q = \{1,..., n\}</math> are involved players, sets <math>X_1,...,X_n</math> are | + | where <math>Q = \{1,..., n\}</math> are involved players, sets <math>X_1,...,X_n</math> are sets of strategies and <math>u_i(x_1,..., x_n)</math> are winnings of the player <math>i</math> for individual strategies. The normal form game is usually represented as a matrix. |
| + | |||
| + | The game for two players in normal form is shown below: | ||
| − | |||
<math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_t \end{matrix}\\ | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_t \end{matrix}\\ | ||
pl. 1, | pl. 1, | ||
| − | \begin{matrix}\mbox{ | + | \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}u_{11} & u_{12} & ... u_{1t} \\u_{21} & u_{22} & ... u_{23} \\u_{k1} & u_{k2} & ... u_{kt} \end{pmatrix}</math> |
| − | Here the player number 1 chose from strategies <math>s_1,..., s_k</math> and the player number 2 chose from strategies <math> t_1,..., t_t</math>. There is an assumption that this is a zero-sum game, and in this game | + | |
| + | Here the player number 1 chose from strategies <math>s_1,..., s_k</math> and the player number 2 chose from strategies <math> t_1,..., t_t</math>. There is an assumption that this is a zero-sum game, and in this game applies: | ||
<math>u_1(s_i,t_j) = -u_2(s_i,t_j)</math> | <math>u_1(s_i,t_j) = -u_2(s_i,t_j)</math> | ||
| Line 60: | Line 85: | ||
and therefore there is need to write only the value of the prize (utility function) for one player. | and therefore there is need to write only the value of the prize (utility function) for one player. | ||
| − | '''Example of the enrolment of the unspecified game''' | + | '''''Note:''' according to the definition of the state space'' |
| + | |||
| + | ''<math>s_k</math> is follower | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>s_i</math> is forerunner'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Example of the enrolment of the unspecified game:''' | ||
<math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ | ||
| − | player 1 | + | player 1 |
\begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}2 & 3\\3 & 4\end{pmatrix}</math> | \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}2 & 3\\3 & 4\end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| − | '''Example of the rock-paper-scissors [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rock-paper-scissors rock-paper-scissors] game''' | + | '''Example of the rock-paper-scissors [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rock-paper-scissors rock-paper-scissors] game:''' |
| + | [[File:RPS.jpg|thumb|right|Rock paper scissors scheme <ref>Rock-paper-scissors. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2014 [cit. 2015-01-25]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rock-paper-scissors</ref>]] | ||
| − | <math>player 2 - R | + | |
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}R & P & S \end{matrix}\\ | ||
pl. 1, | pl. 1, | ||
\begin{matrix}\mbox{R}\\\mbox{P}\\\mbox{S}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1 & -1 \\-1 & 0 & 1 \\1 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}</math> | \begin{matrix}\mbox{R}\\\mbox{P}\\\mbox{S}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1 & -1 \\-1 & 0 & 1 \\1 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| − | Normal form describes possible strategies and winnings of each player and allows the study of the question of optimal strategies. If there is interested in finding a way appropriate strategies there is need to use enrollment of the games in explicit form. | + | Normal form describes possible strategies and winnings of each player and allows the study of the question of optimal strategies. If there is interested in finding a way appropriate strategies there is need to use enrollment of the games in explicit form. <ref name="PELIŠ"/> |
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Extensive form]] game== | ||
| + | Extensive or explicit form of the game is used for the formalization of these games, in which plays a role the order of moves. These games are represented as trees. Each node represents the place where one player chooses stroke and each edge corresponds to a possible move. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NIM.jpg|thumb|right|NIM game in explicit form <ref>Final Review A. In: BURCH, Carl. CSci 150: Foundations of computer science [online]. 2014, May 12 [cit. 2015-01-22]. Dostupné z: http://www.cburch.com/cs/150/</ref>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The notation of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nim NIM] game in explicit form is shown below. In this game of two players at the beginning there are two stacks of two matches. Players are taking turns and they are taken from one of the piles either one or two matches. The player who removes the last match lose the game. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | There are two true sentences: | ||
| + | Every game in explicit form can be transferred to just one game in normal form. | ||
| + | For every game in normal form notation can be found more games in the explicit form. <ref name="PELIŠ"/> <ref name="MORRIS"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Optimal strategies= | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Antagonistic games== | ||
| + | The goal of every rational player is to win the game, other words to maximize their winnings. Consider the only strategy antagonistic games between two players that are written in normal form: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_l \end{matrix}\\ | ||
| + | pl. 1, | ||
| + | \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}u_{11} & u_{12} & ... u_{1l} \\u_{21} & u_{22} & ... u_{23} \\u_{k1} & u_{k2} & ... u_{kl} \end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This matrix reflects values of the player number 1 winning. This player chooses between these strategies (rows <math>i</math> of matrix <math>u (s_i, t_j)</math>) so that his winnings are maximal. | ||
| + | Also he knows that his opponent, player number 2 will choose its strategy to minimize winnings of the player number 1. Player number 1 chooses a strategy s*, for which the minimum value of his winning (in this row) will be the maximal one from all lines. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>s*= max_i, min_j u (s_i, t_j)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The player number 2 progresses analogously. Between its strategies (column j and matrix <math>u (s_i, t_j)</math>) he chooses the strategy t*, for which the maximal value of his loses (in this column) will be the minimal one from all columns. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | It applies that: <math>max_i min_j u (s_i, t_j) \leq < min_j max_i u (s_i, t_j)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> max_i min_j u(s_i, t_j)</math> is called the lower price of the game | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> min_j max_i u(s_i, t_j)</math> is called the upper price of the game | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Example with the equilibrium point==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ player 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}2 & 3\\3 & 4\end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For this normal form game, the equilibrium point takes a form <math>(s_2, t_1)</math>. For the player number 1 is min <math> u(s_1, t_j) = 2</math> and min <math> u(s_2,t_j) = 3</math> and then max min <math>u (s,t) = u(s_2, t_1)</math> what corresponds to strategy <math>s_2</math>. For the player number 2 is max <math> u(s_i, t_1) = 3</math> and max <math>u(s_i, t_2) = 4</math> and then min max <math>u(s,t) = u(s_2,t_1)</math> what corresponds to strategy <math>t_1</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Definition of the saddle point=== | ||
| + | [[File:SP.jpg|thumb|right|Saddle point<ref>Saddle point. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2014 [cit. 2015-01-24]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saddle_point</ref>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | If <math> u(s*, t*) = max_i min_j u(s_i, t_j) = min_j max_i u(s_i, t_j)</math>, there u <math>(s*, t*)</math> i called '''saddle point''' of the matrix and presents the price of the game. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Game theory tries to find the equilibrium point in every game, where players choose strategies. Players choose such strategies, that anyone of them does not have the reason to change its strategy assuming andt that nobody else does change the strategy. If there is a '''point of equilibrium''', optimal strategies of both players are called '''pure strategy''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Example with saddle point==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sometimes the equilibrium point and then the pure strategy does not exist. In the game shown by the matrix below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ player 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}11 & 5\\7 & 9\end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The player number 1 chooses strategy <math>s_2</math>, because for his <math>min_j, u_{ij}</math> the biggest element is <math>u_{21} = 7</math>. The player number 2 chooses strategy <math>t_1</math>, because for his <math>max_i, u{ij}</math> the smallest element is <math>u{21}=9</math>. In this case the lower price of the game is less than the upper price of the game: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>max_i, min_j, u(s_i, t_j) < min_j, max_i u(s_i, t_j).</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | And this game does not have the equilibrium point and that is why there are no pure strategies of the players. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Definition of the mixed strategy=== | ||
| + | Where there is matrix game described of this matrix: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_l \end{matrix}\\ | ||
| + | pl. 1, | ||
| + | \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}u_{11} & u_{12} & ... u_{1l} \\u_{21} & u_{22} & ... u_{23} \\u_{k1} & u_{k2} & ... u_{kl} \end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>p_1 + p_2 + ... + p_k = 1 and p_i >0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | q_1 + q_2 + ...q_l = 1 and q_i > 0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then there is a game with payroll function: | ||
| + | <math> \pi (p, q) = \sum_{i=1}^k \sum_{j=1}^l p_i, u_ij, q_j</math> and it is called '''mixed extension''' of the original game. This mixed extension means, that every participating player chooses from his strategies with certain probability. The mixed strategy is written as the vector of the relevant probabilities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Example with mixed strategy==== | ||
| + | Let's go back to this game: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ pl. 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}11 & 5\\7 & 9\end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mixed strategy of individual players can be found as the extreme of payroll function, that are values '''p''' and '''q''' for which applies that <math> \pi (p, q)</math> will be maximal resp. minimal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> \pi (p,q) = 11 p_1 q_1 + 5 p_1 (1-q_1) + 7 q_1 (1-p_1) + 9 (1-p_1)(1-q_1) = 8 p_1 q_1 - 4 p_1 - 2 q_1 + 9 </math> and there are partial derivations: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial \pi (p, q)}{p_1}= 8 q_1 - 4 = 0</math> and then <math>q_1 = 1/2</math> | ||
| − | == | + | <math>\frac{\partial \pi (p, q)}{q_1}= 8 p_1 - 2 = 0</math> and then <math>p_1 = 1/4</math> |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The player number 1 chooses strategy (1/4, 3/4) and the player number 2 chooses strategy (1/2, 1/2). For these strategies is the price of the game <math> \pi(p,q)</math> maximal and equals to 8. <ref name="PELIŠ"/> |
| + | |||
| + | ==Non-antagonistic games== | ||
| + | In the case of non-antagonistic games the winning of one player is not at the expense on the other one. Players can (cooperative games) or cannot (non-cooperative games) negotiate about their strategies. Double matrix of the winnings | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>player 2 - \begin{matrix} t_1 & ........t_2 & ........... & t_l \end{matrix}\\ | ||
| + | pl. 1 , | ||
| + | \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{..}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix} u_{11}, v_{11} & u_{12}, v_{12} & ... & u_{1l}, v_{1l} \\u_{21}, v_{21} & u_{22}, v_{22} & ... & u_{23}, v_{23} \\... & ... & ... & ... \\ u_{k1}, v_{k1} & u_{k2}, v_{k2} & ... & u_{kl}, v_{kl}\end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The value <math>u_{ij}</math> corresponds to the payroll of the player number 1 in the case of the strategies <math>s_i</math> (player number 1) and <math>t_j</math> (player number 2), the value <math>v_{ij}</math> corresponds to the payroll of the player number 2 in the case of strategies <math>s_i</math> (player number 1) and <math>t_j</math> (player number 2). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Definition of the non-antagonistic game=== | ||
| + | The couple of strategies (s*, t*) is called the equilibrium point, just when: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>u(s, t*) \leq u(s*, t*)</math> for every '''s''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>u(s*, t) \leq v(s*, t*)</math> for every '''t''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let equilibrium point corresponding to the element <math>(u_{ij}, v_{ij})</math>. Then: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>u_{ij} = max_k u_{kj}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>v_{ij} = max_k v_{ik}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Example of the [[Prisoner's dilemma]]==== | ||
| + | The best example of the non-antagonistic game is non-cooperative game Prisoner's dilemma. Where two prisoners are accused of the same crime. | ||
| + | If both of them confess they are both sentenced to 5 years in prison, because the confession is a mitigating circumstance. If both of them deny the crime, they will be both sentenced of the minor delict to 1 year in prison. If only one of them admits, he will be in the role of chief witness acquitted, but the other accused will be sentenced to 10 years in prison. The relevant notation of this game in normal form is shown below. The number in the matrix indicates the length of the sentence. The main goal of the players is to minimize the value of the length of the sentence, or choose a strategy, for which the maximal amount of punishment (for possible strategies for co-accused) is minimal. Then: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The prisoner number 1 <math> s* = min_i max_j u_{ij}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The prisoner number 2 <math> t* = min_j max_i v_{ij}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math> player 2 - \begin{matrix} D & A \end{matrix}\\\\ | ||
| + | pl. 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{D}\\\mbox{A}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix} (1, 1) & (10, 0)\\ (0, 10) & (5, 5) \end{pmatrix}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Based on the equilibrium strategy the best option for both of them is <math>(s*, t*) = (admit, admit)</math>. By looking at the double matrix, we find that the better (in terms of the amount of punishment) would be the strategy <math>(deny, deny)</math> because in this case the amount of the punishment for both prisoners was lower. Hence the name of the game is "dilemma". None of the accused does not know whether his accomplice succumb to temptation confess and go unpunished. <ref name="PELIŠ"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==The search for suitable strategy== | ||
| + | The following chapters show two ways to search for a suitable strategy for antagonistic games - minimax and alpha-beta pruning. Both strategies are shown in the example of the game written in developed form represented by the tree. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are also algorithms for searching trees and the main difference between these algorithms and algorithms for finding strategies during games is that there is no control over all transitions between the nodes of the tree because some of the moves do the opponent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | More precisely: if we consider sequential game of two players, then player A decides at nodes that are even-numbered and player B at nodes that are odd. This method of searching when players have no control over all of their moves is called adversarial search.<ref name="PELIŠ"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Minimax=== | ||
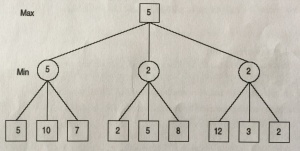
| + | [[File:MM.jpg|thumb|right|MINIMAX<ref name="PELIŠ"/>]] | ||
| + | Minimax strategy for decision making under uncertainty has been described above. | ||
| + | It is based on the principle that assuming the assumption of rationality of the opponent, we choose such a move to make the best subsequent move of the opponent, from our perspective the least dangerous. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The notation consists of the tree, where to each node is assign a value based on the number of wins (value function <math>v</math>) in the sub tree of the node. Each node of the tree is divided into the MAX level (even nodes) and MIN levels (odd nodes). At every MAX level the first player selects the move, which maximize the value of the specified criterion, and at every MIN level the second player, which minimizes the value of that criteria. The criterion is MINIMAX value: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>MINIMAX(n)=\left\{\begin{matrix} u(n), & \mbox{for }n\mbox{ leaf node} \\ max_s MINMAX (s), & \mbox{for }n\mbox{ is MAX node} \\ min_s MINMAX (s), & \mbox{for }n\mbox{ is MIN node}\end{matrix}\right.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where <math>s</math> are all the successors of node <math>n</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Valuing the nodes runs from the bottom - from the leaves representing the final game situation towards the root. In the MINIMAX picture, the player chooses for his move, the MIN, that is first node from the left, which is 5. Then he choose the MIN from second set, it is 2 and then he also chooses the MIN from the third set, which is 2. From these 3 results, he chooses the MAX, which is 5. The result is 5. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Application of MINIMAX assumes, that the whole tree of solution is known. The example from real life is tic-tac-toe.<ref name="PELIŠ"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Alfa-beta pruning=== | ||
| + | [[File:AB.png|thumb|right|Alfa-beta pruning<ref>Alpha–beta pruning. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2015 [cit. 2015-01-22]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha%E2%80%93beta_pruning</ref>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | is modification of the MINIMAX strategy based on the branches method, which allows cuts not perspective parts of the tree. In the algorithm, there are two new values: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\alpha</math> is the biggest known value for the node MAX | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\beta</math> is the smallest known value for the node MIN | ||
| + | |||
| + | Every MAX node is sequentially compared with MINMAX value of individual followers with <math>\beta</math> value and if the MINMAX <math> > \beta</math>, then other followers are not searched. | ||
| + | Every MIN node is sequentially compared with MINMAX value of individual followers with <math>\alfa</math> value and if the MINMAX <math> < \alfa</math>, then other followers are not searched. | ||
| + | The complexity time of alpha-beta pruning is lower than by MINIMAX strategy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Backup file= | ||
| + | [[File:GT.doc]] | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | --[[User:Xgubk00|Xgubk00]] 19:46, 25 January 2015 (CET) | ||
Latest revision as of 19:46, 25 January 2015
| Theory of Games and Economic Behavior |
|---|
| Theory of Games and Economic Behavior, published in 1944 by Princeton University Press, is a book by mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern which is considered the groundbreaking text that created the interdisciplinary research field of game theory. In the introduction of its 60th anniversary commemorative edition from the Princeton University Press, the book is described as "the classic work upon which modern-day game theory is based."
The book is based on prior research by von Neumann, published in 1928 under the German title "Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele" ("On the Theory of Parlor Games"). The derivation of expected utility from its axioms appeared in an appendix to the Second Edition (1947). Von Neumann and Morgenstern used objective probabilities, supposing that all the agents had the same probability distribution, as a convenience. However, von Neumann and Morgenstern mentioned that a theory of subjective probability could be provided, and this task was completed by Johann Pfanzagl in 1967.[1] |
- The Essay topic: Game Theory
- Class:4IT496 Simulation of Systems (WS 2014/2015) [2]
- Author: Kristýna Gubišová
The beginning of mathematical game theory originated in 1944, when the book called Theory of Games and Economic Behavior [3] by mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern was written and published by Princeton University Press. Game theory is the discipline of applied mathematics, that analyzes the spectrum of conflict decision situations that may occur, wherever there is a conflict of interests.
Game theory models try to analyze these conflict situations and by building a mathematical model of the conflict and computing are trying to find the best strategies for specific parties of the conflict.[4]
Game theory is a branch of, originally, applied mathematics, used mostly in economics and political science, a little bit in biology, that gives us a mathematical taxonomy of social life and it predicts what people are likely to do and believe others will do in cases where everyone's actions affect everyone else. That's a lot of things: competition, cooperation, bargaining, games like hide-and-seek, and poker.[5]
Contents
Basic concepts
The basis of most mathematical models of game theory is the assumption of rationality. Every player acts such that he maximizes their profit (their win).
- The player based on stable preferences sets objectives and strategies to elect the most efficient possible to achieve these objectives.
- The player is confronted by a number of situations and he is able to sort them according to their preferences from the most advantageous to the least advantageous.
The assumption of rationality (of each player) is the factor which distinguishes the game theory from the theory of decision.
This alignment must be complete, i. e. must cover all situations and transitive, i. e. if a player prefer the situation A before the situation B and situation C, and must prefer the situation A before the situation C. Based on the preferences of the situation is derived utility function of player. The sole objective of the player is then maximizes the value of the utility function. [6]
Games
All the games that we are considering in this chapter have certain things in common and these are:
Games types
- There is a finite set of players assumed (who may be people, groups of people holding the same opinion, or more abstract entities like computer programs or “nature” or “the house”). The least possible number of players is 2.
- Number of applied strategies may be finite and infinite. For endless strategy plays a role timing of moves. (for game theory consider games with a finite number of strategies)
- Winning types are divided into games with constant sum and games with non-constant sum.
- In constant sum games, the strategy for each option is the sum of payroll functions (winnings) of all players constant - special case of these games are zero-sum games, in which what one player wins, the other player must lose (e. g. chess, tic-tac-toe, popular Chinese game go)
- In non-zero sum games, winning the one player might not necessarily mean losing for another player (e. g. prisoner's dilemma, battle of the buddies, politics)
- The game ends after a finite number of moves.
- Strategic games assumes, that, players will make a one move or decision in the same time (e. g. rock-paper-scissors, prisoner's dilemma)
- Tensile games are based on sequences of moves at which the players take turns (e. g. chess, tic-tac-toe)
- According to available information, there are:
- Games with complete information, each player has complete knowledge of the rules of the game (e. g. chess)
- Games with incomplete information occur very rarely in real life(e. g. poker, prisoner's dilemma, Bayesian game).
- Players cooperation
- In cooperative games, players can eventually build coalitions among themselves or negotiate
- In non-cooperative games is not possible to create a coalition or negotiate
- At different points in the game, each player has a range of choices or moves. This set of choices is finite.
- After the game ends, each player receives a numerical payoff. This number may be negative, in which case it is interpreted as a loss of the absolute value of the number. For example, in a game like chess the payoff for winning might be +1, for losing -1, and for a draw 0.[7]
In addition, the following are properties which a game may or may not have:
- There may be chance moves. In a card game, the dealing of the hands is such a chance move. In chess there are no chance moves.
- In some games, each player knows, at every point in the game the entire previous history of the game. This is true of tic-tac-toe and backgammon but not of bridge (because the cards dealt to the other players are hidden). A game with this property is said to be of perfect information. Note that a game of perfect information may have chance moves. Backgammon is an example of this because a die is rolled at points in the game.[6]
Normal form games
Game in the normal form is defined by set Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \{ Q, X_1, ..., X_n, u_1 (x_1,...X_n),..., u_n (x_1,..., x_n) \}}
where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Q = \{1,..., n\}}
are involved players, sets Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X_1,...,X_n}
are sets of strategies and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u_i(x_1,..., x_n)}
are winnings of the player Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i}
for individual strategies. The normal form game is usually represented as a matrix.
The game for two players in normal form is shown below:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_t \end{matrix}\\ pl. 1, \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}u_{11} & u_{12} & ... u_{1t} \\u_{21} & u_{22} & ... u_{23} \\u_{k1} & u_{k2} & ... u_{kt} \end{pmatrix}}
Here the player number 1 chose from strategies Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_1,..., s_k}
and the player number 2 chose from strategies Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_1,..., t_t}
. There is an assumption that this is a zero-sum game, and in this game applies:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u_1(s_i,t_j) = -u_2(s_i,t_j)}
and therefore there is need to write only the value of the prize (utility function) for one player.
Note: according to the definition of the state space
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_k} is follower
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_i} is forerunner
Example of the enrolment of the unspecified game:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ player 1 \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}2 & 3\\3 & 4\end{pmatrix}}
Example of the rock-paper-scissors rock-paper-scissors game:
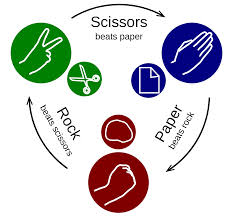
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}R & P & S \end{matrix}\\ pl. 1, \begin{matrix}\mbox{R}\\\mbox{P}\\\mbox{S}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}0 & 1 & -1 \\-1 & 0 & 1 \\1 & -1 & 0 \end{pmatrix}}
Normal form describes possible strategies and winnings of each player and allows the study of the question of optimal strategies. If there is interested in finding a way appropriate strategies there is need to use enrollment of the games in explicit form. [6]
Extensive form game
Extensive or explicit form of the game is used for the formalization of these games, in which plays a role the order of moves. These games are represented as trees. Each node represents the place where one player chooses stroke and each edge corresponds to a possible move.
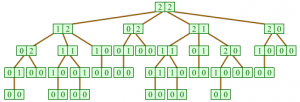
The notation of the NIM game in explicit form is shown below. In this game of two players at the beginning there are two stacks of two matches. Players are taking turns and they are taken from one of the piles either one or two matches. The player who removes the last match lose the game.
There are two true sentences:
Every game in explicit form can be transferred to just one game in normal form.
For every game in normal form notation can be found more games in the explicit form. [6] [7]
Optimal strategies
Antagonistic games
The goal of every rational player is to win the game, other words to maximize their winnings. Consider the only strategy antagonistic games between two players that are written in normal form:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_l \end{matrix}\\ pl. 1, \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}u_{11} & u_{12} & ... u_{1l} \\u_{21} & u_{22} & ... u_{23} \\u_{k1} & u_{k2} & ... u_{kl} \end{pmatrix}}
This matrix reflects values of the player number 1 winning. This player chooses between these strategies (rows Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i}
of matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u (s_i, t_j)}
) so that his winnings are maximal.
Also he knows that his opponent, player number 2 will choose its strategy to minimize winnings of the player number 1. Player number 1 chooses a strategy s*, for which the minimum value of his winning (in this row) will be the maximal one from all lines.
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s*= max_i, min_j u (s_i, t_j)}
The player number 2 progresses analogously. Between its strategies (column j and matrix Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u (s_i, t_j)} ) he chooses the strategy t*, for which the maximal value of his loses (in this column) will be the minimal one from all columns.
It applies that: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle max_i min_j u (s_i, t_j) \leq < min_j max_i u (s_i, t_j)}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle max_i min_j u(s_i, t_j)} is called the lower price of the game
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle min_j max_i u(s_i, t_j)} is called the upper price of the game
Example with the equilibrium point
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ player 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}2 & 3\\3 & 4\end{pmatrix}}
For this normal form game, the equilibrium point takes a form Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (s_2, t_1)} . For the player number 1 is min Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s_1, t_j) = 2} and min Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s_2,t_j) = 3} and then max min Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u (s,t) = u(s_2, t_1)} what corresponds to strategy Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_2} . For the player number 2 is max Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s_i, t_1) = 3} and max Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s_i, t_2) = 4} and then min max Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s,t) = u(s_2,t_1)} what corresponds to strategy Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_1} .
Definition of the saddle point
If Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s*, t*) = max_i min_j u(s_i, t_j) = min_j max_i u(s_i, t_j)} , there u Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (s*, t*)} i called saddle point of the matrix and presents the price of the game.
Game theory tries to find the equilibrium point in every game, where players choose strategies. Players choose such strategies, that anyone of them does not have the reason to change its strategy assuming andt that nobody else does change the strategy. If there is a point of equilibrium, optimal strategies of both players are called pure strategy
Example with saddle point
Sometimes the equilibrium point and then the pure strategy does not exist. In the game shown by the matrix below:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ player 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}11 & 5\\7 & 9\end{pmatrix}}
The player number 1 chooses strategy Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_2} , because for his Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle min_j, u_{ij}} the biggest element is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u_{21} = 7} . The player number 2 chooses strategy Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_1} , because for his Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle max_i, u{ij}} the smallest element is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u{21}=9} . In this case the lower price of the game is less than the upper price of the game:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle max_i, min_j, u(s_i, t_j) < min_j, max_i u(s_i, t_j).}
And this game does not have the equilibrium point and that is why there are no pure strategies of the players.
Definition of the mixed strategy
Where there is matrix game described of this matrix:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2 & t_l \end{matrix}\\ pl. 1, \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}u_{11} & u_{12} & ... u_{1l} \\u_{21} & u_{22} & ... u_{23} \\u_{k1} & u_{k2} & ... u_{kl} \end{pmatrix}}
Let Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_1 + p_2 + ... + p_k = 1 and p_i >0 q_1 + q_2 + ...q_l = 1 and q_i > 0}
Then there is a game with payroll function: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi (p, q) = \sum_{i=1}^k \sum_{j=1}^l p_i, u_ij, q_j} and it is called mixed extension of the original game. This mixed extension means, that every participating player chooses from his strategies with certain probability. The mixed strategy is written as the vector of the relevant probabilities.
Example with mixed strategy
Let's go back to this game:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix}t_1 & t_2\end{matrix}\\\\ pl. 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s1}\\\mbox{s2}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix}11 & 5\\7 & 9\end{pmatrix}}
Mixed strategy of individual players can be found as the extreme of payroll function, that are values p and q for which applies that Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi (p, q)} will be maximal resp. minimal.
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi (p,q) = 11 p_1 q_1 + 5 p_1 (1-q_1) + 7 q_1 (1-p_1) + 9 (1-p_1)(1-q_1) = 8 p_1 q_1 - 4 p_1 - 2 q_1 + 9 } and there are partial derivations:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial \pi (p, q)}{p_1}= 8 q_1 - 4 = 0}
and then Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q_1 = 1/2}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial \pi (p, q)}{q_1}= 8 p_1 - 2 = 0} and then Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_1 = 1/4}
The player number 1 chooses strategy (1/4, 3/4) and the player number 2 chooses strategy (1/2, 1/2). For these strategies is the price of the game Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pi(p,q)} maximal and equals to 8. [6]
Non-antagonistic games
In the case of non-antagonistic games the winning of one player is not at the expense on the other one. Players can (cooperative games) or cannot (non-cooperative games) negotiate about their strategies. Double matrix of the winnings
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix} t_1 & ........t_2 & ........... & t_l \end{matrix}\\ pl. 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{s 1}\\\mbox{s 2}\\\mbox{..}\\\mbox{s k}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix} u_{11}, v_{11} & u_{12}, v_{12} & ... & u_{1l}, v_{1l} \\u_{21}, v_{21} & u_{22}, v_{22} & ... & u_{23}, v_{23} \\... & ... & ... & ... \\ u_{k1}, v_{k1} & u_{k2}, v_{k2} & ... & u_{kl}, v_{kl}\end{pmatrix}}
The value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u_{ij}}
corresponds to the payroll of the player number 1 in the case of the strategies Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_i}
(player number 1) and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_j}
(player number 2), the value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v_{ij}}
corresponds to the payroll of the player number 2 in the case of strategies Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_i}
(player number 1) and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_j}
(player number 2).
Definition of the non-antagonistic game
The couple of strategies (s*, t*) is called the equilibrium point, just when:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s, t*) \leq u(s*, t*)} for every s
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u(s*, t) \leq v(s*, t*)} for every t
Let equilibrium point corresponding to the element Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (u_{ij}, v_{ij})} . Then:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u_{ij} = max_k u_{kj}}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v_{ij} = max_k v_{ik}}
Example of the Prisoner's dilemma
The best example of the non-antagonistic game is non-cooperative game Prisoner's dilemma. Where two prisoners are accused of the same crime. If both of them confess they are both sentenced to 5 years in prison, because the confession is a mitigating circumstance. If both of them deny the crime, they will be both sentenced of the minor delict to 1 year in prison. If only one of them admits, he will be in the role of chief witness acquitted, but the other accused will be sentenced to 10 years in prison. The relevant notation of this game in normal form is shown below. The number in the matrix indicates the length of the sentence. The main goal of the players is to minimize the value of the length of the sentence, or choose a strategy, for which the maximal amount of punishment (for possible strategies for co-accused) is minimal. Then:
The prisoner number 1 Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s* = min_i max_j u_{ij}}
The prisoner number 2 Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t* = min_j max_i v_{ij}}
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle player 2 - \begin{matrix} D & A \end{matrix}\\\\ pl. 1 , \begin{matrix}\mbox{D}\\\mbox{A}\end{matrix} \begin{pmatrix} (1, 1) & (10, 0)\\ (0, 10) & (5, 5) \end{pmatrix}}
Based on the equilibrium strategy the best option for both of them is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (s*, t*) = (admit, admit)}
. By looking at the double matrix, we find that the better (in terms of the amount of punishment) would be the strategy Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (deny, deny)}
because in this case the amount of the punishment for both prisoners was lower. Hence the name of the game is "dilemma". None of the accused does not know whether his accomplice succumb to temptation confess and go unpunished. [6]
The search for suitable strategy
The following chapters show two ways to search for a suitable strategy for antagonistic games - minimax and alpha-beta pruning. Both strategies are shown in the example of the game written in developed form represented by the tree.
There are also algorithms for searching trees and the main difference between these algorithms and algorithms for finding strategies during games is that there is no control over all transitions between the nodes of the tree because some of the moves do the opponent.
More precisely: if we consider sequential game of two players, then player A decides at nodes that are even-numbered and player B at nodes that are odd. This method of searching when players have no control over all of their moves is called adversarial search.[6]
Minimax
Minimax strategy for decision making under uncertainty has been described above. It is based on the principle that assuming the assumption of rationality of the opponent, we choose such a move to make the best subsequent move of the opponent, from our perspective the least dangerous.
The notation consists of the tree, where to each node is assign a value based on the number of wins (value function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v} ) in the sub tree of the node. Each node of the tree is divided into the MAX level (even nodes) and MIN levels (odd nodes). At every MAX level the first player selects the move, which maximize the value of the specified criterion, and at every MIN level the second player, which minimizes the value of that criteria. The criterion is MINIMAX value:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle MINIMAX(n)=\left\{\begin{matrix} u(n), & \mbox{for }n\mbox{ leaf node} \\ max_s MINMAX (s), & \mbox{for }n\mbox{ is MAX node} \\ min_s MINMAX (s), & \mbox{for }n\mbox{ is MIN node}\end{matrix}\right.}
where Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s} are all the successors of node Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} .
Valuing the nodes runs from the bottom - from the leaves representing the final game situation towards the root. In the MINIMAX picture, the player chooses for his move, the MIN, that is first node from the left, which is 5. Then he choose the MIN from second set, it is 2 and then he also chooses the MIN from the third set, which is 2. From these 3 results, he chooses the MAX, which is 5. The result is 5.
Application of MINIMAX assumes, that the whole tree of solution is known. The example from real life is tic-tac-toe.[6]
Alfa-beta pruning
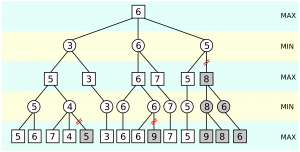
is modification of the MINIMAX strategy based on the branches method, which allows cuts not perspective parts of the tree. In the algorithm, there are two new values:
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha} is the biggest known value for the node MAX
Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} is the smallest known value for the node MIN
Every MAX node is sequentially compared with MINMAX value of individual followers with Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} value and if the MINMAX Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle > \beta} , then other followers are not searched. Every MIN node is sequentially compared with MINMAX value of individual followers with Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alfa} value and if the MINMAX Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle < \alfa} , then other followers are not searched. The complexity time of alpha-beta pruning is lower than by MINIMAX strategy.
Backup file
References
- ↑ Theory of Games and Economic Behavior. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-, 2014 [cit. 2015-01-22]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory_of_Games_and_Economic_Behavior
- ↑ ŠALAMON, Tomáš. Design of agent-based models: developing computer simulations for a better understanding of social processes. Řepín-Živonín: Tomáš Bruckner, 2011. ISBN 978-809-0466-111.
- ↑ COPELAND, A. H. (1945). "Review: Theory of Games and Economic Behavior by John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern". Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 51 (07): 498–504. doi:10.1090/s0002-9904-1945-08391-8.
- ↑ Teorie her. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2014 [cit. 2015-01-25]. Dostupné z: http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Teorie_her
- ↑ CAMERER, C. (January 2013). TEDX. Acquired in January 2014, z <http://www.ted.com/talks/colin_camerer_neuroscience_game_theory_monkeys?language=en/>
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 [PELIŠ, Michal: Teorie her jako formální teorie racionálního rozhodování (Game theory as a formal theory of rational decision-making); In: Soudobá sociologie II (Teorie sociálního jednání a sociální struktury). 1 vyd. 2008, Praha: Karolinum; s. 255-276. ISBN 978-80-246-1413-7. ]
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 [MORRIS, Peter. Introduction to game theory. New York: Springer-Verlag, c1994, xvi, 230 p. ISBN 03-879-4284-X.]
- ↑ Rock-paper-scissors. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2014 [cit. 2015-01-25]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rock-paper-scissors
- ↑ Final Review A. In: BURCH, Carl. CSci 150: Foundations of computer science [online]. 2014, May 12 [cit. 2015-01-22]. Dostupné z: http://www.cburch.com/cs/150/
- ↑ Saddle point. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2014 [cit. 2015-01-24]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saddle_point
- ↑ Alpha–beta pruning. In: Wikipedia: the free encyclopedia [online]. San Francisco (CA): Wikimedia Foundation, 2001-2015 [cit. 2015-01-22]. Dostupné z: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha%E2%80%93beta_pruning
--Xgubk00 19:46, 25 January 2015 (CET)
