Difference between revisions of "Casual loop diagram"
(→Problem of CLDs) |
|||
| (70 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | *'''The Essay topic''': | + | *'''The Essay topic''': Causal loop diagram |
*'''Class''':[http://isis.vse.cz/katalog/syllabus.pl?predmet=95726;zpet=..%2Fpracoviste%2Fpredmety.pl%3Fid%3D64%2Clang%3Dcz;jazyk=1;lang=sk 4IT496 Simulation of Systems] (WS 2014/2015) | *'''Class''':[http://isis.vse.cz/katalog/syllabus.pl?predmet=95726;zpet=..%2Fpracoviste%2Fpredmety.pl%3Fid%3D64%2Clang%3Dcz;jazyk=1;lang=sk 4IT496 Simulation of Systems] (WS 2014/2015) | ||
*'''Author''': Martina Nováková | *'''Author''': Martina Nováková | ||
| − | + | = Introduction = | |
Everything is connected to everything else. It doesn´t matter if it is nature or human environment, there is a large and complex web of interactions. But sometimes we need only sections of these connections, and so we have to isolate issues which we would like to describe and observe. There are different word and arrow diagrams, e.g. causal-loop diagrams, cognitive maps or fishbone diagrams. They are widespread in system dynamics. This chapter is concentrated on issue of causal loop diagrams. (Haraldsson, 2000) | Everything is connected to everything else. It doesn´t matter if it is nature or human environment, there is a large and complex web of interactions. But sometimes we need only sections of these connections, and so we have to isolate issues which we would like to describe and observe. There are different word and arrow diagrams, e.g. causal-loop diagrams, cognitive maps or fishbone diagrams. They are widespread in system dynamics. This chapter is concentrated on issue of causal loop diagrams. (Haraldsson, 2000) | ||
| − | + | = Description of causal loop diagrams = | |
Causal loop diagrams (CLDs) are a very simple but powerful way of visualizing important parts of the system and how they interrelate. It is a great tool for dealing with complex problems and the striking component of system dynamics. | Causal loop diagrams (CLDs) are a very simple but powerful way of visualizing important parts of the system and how they interrelate. It is a great tool for dealing with complex problems and the striking component of system dynamics. | ||
| − | Causal loop diagrams are useful for displaying the behaviour of cause and effect from system standpoint. | + | Causal loop diagrams are '''useful for displaying the behaviour of cause and effect from system standpoint.''' |
| − | As stated above there are other tools which are used for modelling of system dynamics. One of them which could seem the same as | + | CLDs are excellent for (Sterman, 2000): |
| + | |||
| + | ''•Quickly capturing your hypotheses about the causes of dynamics;'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''•Eliciting and capturing the mental models of individuals or teams;'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''•Communicating the important feedbacks you believe are responsible for a problem.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | They show the interrelation between causes and their effects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As stated above there are other tools which are used for modelling of system dynamics. One of them which could seem the same as causal loop diagram is a Fishbone diagram (or we can call it Cause and effect diagram). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Fishbone.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Example of Fishbone diagram]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | But fishbone diagram is different because it can induce categories of causes that impact a problem. Although CLDs focuses on causation too, there are differences because CLDs are more general and more expressive than fishbone (Osgood, 2004). After finishing CLD diagram there is diagram of the negative and positive reinforcements. | ||
The main principle of the Causal loop diagram is quite simple. Parts of a system are visualized using textual identifies. The connections between the parts are shown using arrows pointing in the direction of influence. Creating the causal loop diagram with given system is actually quite simple. we start with the parts we already know and keep asking what influences this part has until we reach parts that are at the systems boundary. There are all parts that do not change. Then you go in the other direction and keep asking which other parts of the system influence this part If that part is already there you connect it otherwise you create a new part. | The main principle of the Causal loop diagram is quite simple. Parts of a system are visualized using textual identifies. The connections between the parts are shown using arrows pointing in the direction of influence. Creating the causal loop diagram with given system is actually quite simple. we start with the parts we already know and keep asking what influences this part has until we reach parts that are at the systems boundary. There are all parts that do not change. Then you go in the other direction and keep asking which other parts of the system influence this part If that part is already there you connect it otherwise you create a new part. | ||
| + | |||
==Symbols of CLDs== | ==Symbols of CLDs== | ||
| + | CLD consists of nodes which represent variables and arrows represent realationship between them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There will be explained main symbols of causal loops and procedure of their creation. If we want to put system in practise, we have to follow some rules. There are several causal loop concepts (Haraldsson, 2000). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''The arrow''' is used to show causation. The item at the tail of the arrow influences the item at the head of the arrow. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The + sign''' near the arrowhead signifies that an increase (or decrease) in the first variable increase (decrease) the following variable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The – sign''' near the arrowhead signifies that an increase | ||
| + | (decreases) in hte first variable decrease(increase) the following variable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The symbol B''', which is in the middle of a loop, signifies that the loop moves away from equilibrium point. This loop continuous going in the same direct. This is called a positive feedback loop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The symbol R''', which is in the middle of a loop, signifies changing direction of the loop. It means that the system move toward equilibrium. This is called a negative feedback loop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Two hash marks''' on the causal loop represent a delay. It is a situation to take time before the effect plays out. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | You can see all these symbols and hash marks in the picture describing very simply population. In this diagram we can see that two things which change population is death and birth. More births causes the population to increase and more deaths leading to decrease population. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Population.jpg|none|framed|'''Causal loop diagram describing very simply population. (Zhou, 2012)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Types of feedback loops= | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because systems are always running circular in organizations, they formed feedback loops. We should state, what does the word feedback loop means exactly. In many cases changing one factor will impact another factor (there is some affect). This factor will again affect the first one (there is some cause). Because of this it is called feedback loop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are two main types of feedback loops which are called positive and negative feedback loops. All loops will be explained with an example and there will be stated their dynamic behaviourin the next chapter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Positive feedback loop == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This loop is called a reinforcing or amplifying loop and leads to growth at an ever-increasing rate. It is called as exponential growth in graph. | ||
| + | The reinforcing loop is typical for population growth. When population goes up, births go up. As we can see on the picture a loop goes always round until there is a hit limit (but this is not usually shown). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another example of the positive feedback loop is a theatre trying to improve its profitability. If the theatre gives more investments in a production there could be better plays and more famous actors. If there will be famous actors, more people start to visit the theathre and there will be higher ticket sales (Mind Tools Ltd, 2014) (Harich, and other, 2014). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:PosF.jpg|none|framed|'''Positive feedback loop - Example of Population growth (Harich, and other, 2014)"''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Negative feedback loop == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This loop is called a balancing or goal-seeking loop because it looks for a goal. It means if the actual state of the variable doesn’t reach the goal the loop structure pushes its value up. On the other side if the variable is above goal, it pushes it down. An example of this loop is a thermostat which you can see on picture below. The princip of thermostat is that if is the temperature in the room higher (or lower) than is set, the thermostat increase (or decrease) the actual temperature. Another example is situation of under-resourced service company which wants to raise quality. Although better quality of services directs to improved customer satisfaction (and leads to an increase in demand), the company has not too much time for customers and this influences its ability to improve quality. So the number of customers again decreases. (Mind Tools Ltd, 2014) (Harich, andother, 2014). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NegativeF.jpg|none|framed|'''Negative feedback loop – Example of Thermostat (Harich, and other, 2014)"''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Other cases of feedback loops == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other special cases of loops are '''''negative feedback loops with delay''''' and '''''combination of positive and negative loops'''''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Dynamic behaviour of negative feedback loops with delay''' can direct to oscillation. The amplitude of Oscillation can last indefinitely, or in the other example oscillation could gradually decrease. The amplitude of the oscillation decreases if the variable towards to the goal. An example of the gradually decreasing amplitude of oscillation is distribution systems (Kirkwood, 2013).This situation with a delay we cant usually anticipate, because we dont now how long does the period take. We can use the very good example when we take a shower. There is some seconds, when the water is cold after turn on the faucet. We turn a faucet wide open, but when hot water comes it is too hot that we have to again turn it off and so on. Until we dont get the comfortable shower with an optimal temperature. Simulation of this process is illustrates below(Haraldsson, 2000). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Water.jpg|none|framed|'''The optimalisation of temperature (Haraldsson, 2000)''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Positive and negative feedback loops''' usually don’t work distinctly. They can be combined. Dynamics behaviour of combination of positive and negative loops towards to different patterns. (Kirkwood, 2013). This is typical for biochemical switches. They have to work together cause they have to make special flexible system. On the picture we can see that at first there leads positive feedback loops. It towards to exponential growth. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Creating CLDs= | ||
| + | This part is derived from (Kirkwood, 2013) and (American Creativity Association, 2014). There is no integrated process to drawing a causal loop diagram. But we can accept some reccomendation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 1) At first we have to start with the problem. We have to understand and define the problem which shall be solved. This is necessary to start with. We should ask what is wrong and what the root source of the problem is. When we want to find a cause ask why, to find effect ask what happens. When we are thinking about elements of the causal loop diagram we should use nouns and noun phrases. We should use e.g. only orders, inventory and delivery delay instead of rising orders, falling orders, falling inventory and so on because it is more well-arranged. This example you can see on the picture below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Creat1.jpg|none|framed|'''The Well-aranged causal loop (Haraldsson, 2000)''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2) Describe relations between a cause and effects. Bear in mind constantly that + and – doesn’t mean bad or good. Plus is used for intensification and minus is used for diminishing effects. | ||
| + | When we construct links, we should expect that there can be other possible unexpected sides. We should think about adding this links for representing side effects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3) When we draw negative feedback, it is usually comprehensible if there is existing gap which directs toward the goal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4) In many examples we can accept that there is delay when the actual state is perceived. For this situation it could be important if we include the causal loop diagram for the actual value and the perceived value. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5) In many causal loop diagrams there is no difference between long and short result or process. And this is not so right, because you should make difference between these two states. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6) If you think that the links between two elements are hard to say in a simple way, you should use more simple intermediate elements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Creat2.jpg|none|framed|'''Using more elemets in causal loop diagram (Haraldsson, 2000)''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7) For someone who is reading your diagram is necessary to have it in a simple form. There hasn’t be illustrated every detail. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =CLDs in practise and their problems= | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are many practises of causal loop diagrams in business or workacademy but there are some problems around this diagrams too. We talk about both belove with some examples. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == CLD in practise == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Practise.jpg|400px|thumb|right|'''Causal loop diagram of every day tasks (Transentis Consulting, 2014)"''']] | ||
| + | We can ask how the causal loop diagram is useful in practise. If we develop it and present it carefully, it can be very useful for us. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can find very successful CLDs in practise. The most popular example are CLDs of population growth (it could be people or animals or both, that doesn’t matter) and resources diagrams. In the population growth diagram we can control how Immigration and the Birth and death rate change over time. There could be a more extensive demographic example with different age groups and other factors (Halbleib, 2014). | ||
| + | |||
| + | But there are other examples of great using of CLDs. CLDs can be useful in causal modelling to understand organizations and businesses. This is trend in the recent years. CLDs are used in business prototyping, where we can model productivity and causes which influence it, e.g. remaining time, schedule pressure, deadline and so on. This causal loop diagram can be seen on picture (Transentis Consulting, 2014). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Other examples of Causal loop diagrams are in medicine, biology or environment. We can demonstrate it on the causal loop diagram of the dynamics of diabetes. The picture and detailed description you can see in (Fonseca i Casas, 2014) or global warming system. There is a possibility to describe cases and effects of fish pond ecosystem by CLDs. PA Consulting Group created CLDs called “Afghanistan Stability / COIN Dynamics“. It is really extensive diagram summarized a snapshot of U.S. military´s plan (PA Consulting Group, 2010). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Problem of CLDs== | ||
| + | |||
| + | For many types of examples it is clearer to use a hybrid diagram which contains stock-flow chain. But this could be harder for visual language. There are many problems with notation too. There is not uniform labelling. Sometimes it is used an “s” (means “same”) and “o” (means “opposite”) instead of the + and -. This problem is explained by George Richardson in his paper “Problems with causal loop diagrams” and his conclusion is that it is not good to use “s” and “o” because it is less confusing. (Richardson, 1986) . | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Conclusion= | ||
| + | In this paper there was desribe causal loop diagram, its creating and using in practise. As we could se CLDs are quite popular diagrams in practise and are widely used. We can use them in business but in academic work too. For their user it is easy to start drawing these diagrams because all you need to draw CLDs is pencil and paper or a whiteboard. There are to many softwares we can use for drawing this type of diagram too, e.g. Vensimo (for free), STELLA (free, but only for 30 days trial) or AnyLogic (free trial) and other software. As it is was said in the chapter "Problems of CLDs", sometimes it can be problem to make causal loop diagram because of various notations. But CLDs can be very help-full still. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Tasks= | ||
| + | There are two tasks to practise problem of causal loop diagram. Below there are answers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Questions== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1) Try to illustrated causal loop diagram in the picture dealing with zebras and lions.There are help in the form of preddefined words which should be used in the causal loop diagram.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Q1.png|600px|none|left|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | '''2) Try to draw your own causal loop diagram which is contained from demand, profits, price, market expecations and other things around this thematics.''' | |
| − | == | + | == Answers == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Answer for question number 1.'' | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:A1.png|500px|none|left|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Answer for question number 2'' - example how this casual loop diagram could look like. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:A2.png|500px|none|left|]] | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | American Creativity Association. 2014. Causal loop diagram. American Creativity Association. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 27 December 2014.] http://www.amcreativityassoc.org/Resources/Documents/CausalLoopDiagrams.pdf. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fonseca i Casas, Pau. 2014. Formal Language for Computer Simulation:Transdisciplinary Models and Applica\\Ction. Hershey : IGI Global, 2014. 978-1-4666-4370-3. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Halbleib, Harold. 2014. System Models & Simulation. http://www.projectperfect.com.au/. [Online] 7 November 2014. [Cited: 30 December 2014.] | ||
| + | http://www.projectperfect.com.au/info_system_models_and_simulation.php. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Haraldsson, Hördur V. 2000. Introduction to Systems and Causal Loop Diagrams. Lunds Universitet. [Online] January 2000. [Cited: 30. December 2014.] http://cmap.crs.org.pl:4444/rid=1244140954250_1167059429_1461/Introduction%20to%20Systems%20and%20Causal%20Loop%20Diagrams.pdf. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Harich, Jack and Bangerter, Philip. 2014. Feedback Loop. http://www.thwink.org/. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 29 December 2014.] http://www.thwink.org/sustain/glossary/FeedbackLoop.htm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kirkwood, Craig W. 2013. System behaviour and causal loop diagram. Arizona State University. [Online] 12 January 2013. [Cited: 28 December 2014.] http://www.public.asu.edu/~kirkwood/sysdyn/SDIntro/ch-1.pdf. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Mind Tools Ltd. 2014. Systems Diagrams - Understanding How Factors Affect One Another. http://www.mindtools.com/. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 29 December 2014.] http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_04.htm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Osgood, Nathaniel. 2004. Problem Diagnosis & Introduction to Project Dynamics. http://ocw.mit.edu/index.htm. [Online] 13 April 2004. [Cited: 28 December 2014.] http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/civil-and-environmental-engineering/1-040-project-management-spring-2004/lecture-notes/l16diagnsprjctrl.pdf. | ||
| + | |||
| + | PA Consulting Group. 2010. Afganistan Dynamic Planning. MSNBC media. [Online] 2010. [Cited: 28 December 2014.http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/i/MSNBC/Components/Photo/_new/Afghanistan_Dynamic_Planning.pdf.. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Richardson, George P. 1986. Problems with causal-loop diagrams. System thinking. [Online] 1986. [Cited: 29 December 2014.] http://www.systems-thinking.org/intst/d-3312.pdf. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Transentis Consulting. 2014. Causal Loop Diagrams. Business prototyping blog. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 30 December 2014.] http://www.business-prototyping.com/step-by-step-tutorials/. | ||
| + | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:26, 25 January 2015
- The Essay topic: Causal loop diagram
- Class:4IT496 Simulation of Systems (WS 2014/2015)
- Author: Martina Nováková
Contents
Introduction
Everything is connected to everything else. It doesn´t matter if it is nature or human environment, there is a large and complex web of interactions. But sometimes we need only sections of these connections, and so we have to isolate issues which we would like to describe and observe. There are different word and arrow diagrams, e.g. causal-loop diagrams, cognitive maps or fishbone diagrams. They are widespread in system dynamics. This chapter is concentrated on issue of causal loop diagrams. (Haraldsson, 2000)
Description of causal loop diagrams
Causal loop diagrams (CLDs) are a very simple but powerful way of visualizing important parts of the system and how they interrelate. It is a great tool for dealing with complex problems and the striking component of system dynamics.
Causal loop diagrams are useful for displaying the behaviour of cause and effect from system standpoint.
CLDs are excellent for (Sterman, 2000):
•Quickly capturing your hypotheses about the causes of dynamics;
•Eliciting and capturing the mental models of individuals or teams;
•Communicating the important feedbacks you believe are responsible for a problem.
They show the interrelation between causes and their effects.
As stated above there are other tools which are used for modelling of system dynamics. One of them which could seem the same as causal loop diagram is a Fishbone diagram (or we can call it Cause and effect diagram).
But fishbone diagram is different because it can induce categories of causes that impact a problem. Although CLDs focuses on causation too, there are differences because CLDs are more general and more expressive than fishbone (Osgood, 2004). After finishing CLD diagram there is diagram of the negative and positive reinforcements.
The main principle of the Causal loop diagram is quite simple. Parts of a system are visualized using textual identifies. The connections between the parts are shown using arrows pointing in the direction of influence. Creating the causal loop diagram with given system is actually quite simple. we start with the parts we already know and keep asking what influences this part has until we reach parts that are at the systems boundary. There are all parts that do not change. Then you go in the other direction and keep asking which other parts of the system influence this part If that part is already there you connect it otherwise you create a new part.
Symbols of CLDs
CLD consists of nodes which represent variables and arrows represent realationship between them.
There will be explained main symbols of causal loops and procedure of their creation. If we want to put system in practise, we have to follow some rules. There are several causal loop concepts (Haraldsson, 2000).
The arrow is used to show causation. The item at the tail of the arrow influences the item at the head of the arrow.
The + sign near the arrowhead signifies that an increase (or decrease) in the first variable increase (decrease) the following variable.
The – sign near the arrowhead signifies that an increase (decreases) in hte first variable decrease(increase) the following variable.
The symbol B, which is in the middle of a loop, signifies that the loop moves away from equilibrium point. This loop continuous going in the same direct. This is called a positive feedback loop.
The symbol R, which is in the middle of a loop, signifies changing direction of the loop. It means that the system move toward equilibrium. This is called a negative feedback loop.
Two hash marks on the causal loop represent a delay. It is a situation to take time before the effect plays out.
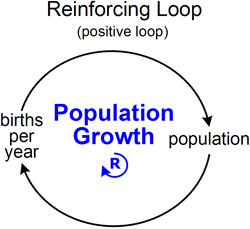
You can see all these symbols and hash marks in the picture describing very simply population. In this diagram we can see that two things which change population is death and birth. More births causes the population to increase and more deaths leading to decrease population.
Types of feedback loops
Because systems are always running circular in organizations, they formed feedback loops. We should state, what does the word feedback loop means exactly. In many cases changing one factor will impact another factor (there is some affect). This factor will again affect the first one (there is some cause). Because of this it is called feedback loop.
There are two main types of feedback loops which are called positive and negative feedback loops. All loops will be explained with an example and there will be stated their dynamic behaviourin the next chapter.
Positive feedback loop
This loop is called a reinforcing or amplifying loop and leads to growth at an ever-increasing rate. It is called as exponential growth in graph. The reinforcing loop is typical for population growth. When population goes up, births go up. As we can see on the picture a loop goes always round until there is a hit limit (but this is not usually shown).
Another example of the positive feedback loop is a theatre trying to improve its profitability. If the theatre gives more investments in a production there could be better plays and more famous actors. If there will be famous actors, more people start to visit the theathre and there will be higher ticket sales (Mind Tools Ltd, 2014) (Harich, and other, 2014).
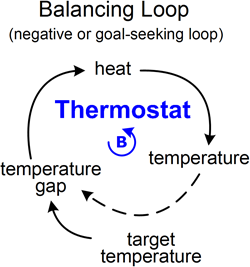
Negative feedback loop
This loop is called a balancing or goal-seeking loop because it looks for a goal. It means if the actual state of the variable doesn’t reach the goal the loop structure pushes its value up. On the other side if the variable is above goal, it pushes it down. An example of this loop is a thermostat which you can see on picture below. The princip of thermostat is that if is the temperature in the room higher (or lower) than is set, the thermostat increase (or decrease) the actual temperature. Another example is situation of under-resourced service company which wants to raise quality. Although better quality of services directs to improved customer satisfaction (and leads to an increase in demand), the company has not too much time for customers and this influences its ability to improve quality. So the number of customers again decreases. (Mind Tools Ltd, 2014) (Harich, andother, 2014).
Other cases of feedback loops
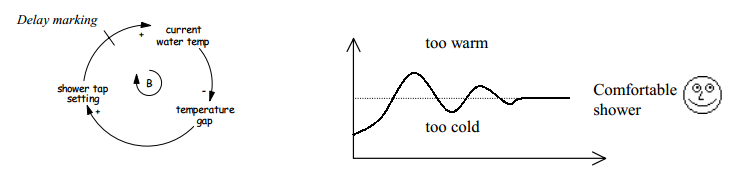
Other special cases of loops are negative feedback loops with delay and combination of positive and negative loops.
Dynamic behaviour of negative feedback loops with delay can direct to oscillation. The amplitude of Oscillation can last indefinitely, or in the other example oscillation could gradually decrease. The amplitude of the oscillation decreases if the variable towards to the goal. An example of the gradually decreasing amplitude of oscillation is distribution systems (Kirkwood, 2013).This situation with a delay we cant usually anticipate, because we dont now how long does the period take. We can use the very good example when we take a shower. There is some seconds, when the water is cold after turn on the faucet. We turn a faucet wide open, but when hot water comes it is too hot that we have to again turn it off and so on. Until we dont get the comfortable shower with an optimal temperature. Simulation of this process is illustrates below(Haraldsson, 2000).
Positive and negative feedback loops usually don’t work distinctly. They can be combined. Dynamics behaviour of combination of positive and negative loops towards to different patterns. (Kirkwood, 2013). This is typical for biochemical switches. They have to work together cause they have to make special flexible system. On the picture we can see that at first there leads positive feedback loops. It towards to exponential growth.
Creating CLDs
This part is derived from (Kirkwood, 2013) and (American Creativity Association, 2014). There is no integrated process to drawing a causal loop diagram. But we can accept some reccomendation.
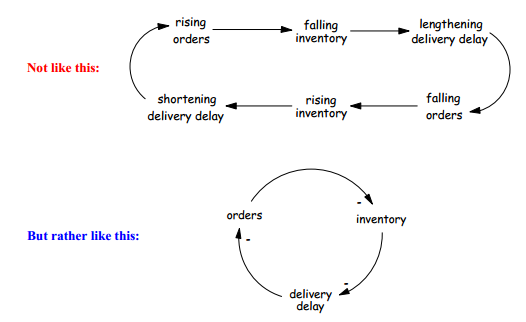
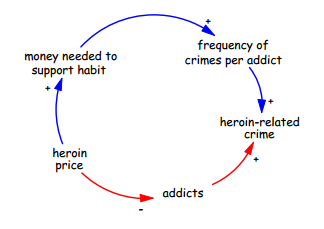
1) At first we have to start with the problem. We have to understand and define the problem which shall be solved. This is necessary to start with. We should ask what is wrong and what the root source of the problem is. When we want to find a cause ask why, to find effect ask what happens. When we are thinking about elements of the causal loop diagram we should use nouns and noun phrases. We should use e.g. only orders, inventory and delivery delay instead of rising orders, falling orders, falling inventory and so on because it is more well-arranged. This example you can see on the picture below.
2) Describe relations between a cause and effects. Bear in mind constantly that + and – doesn’t mean bad or good. Plus is used for intensification and minus is used for diminishing effects. When we construct links, we should expect that there can be other possible unexpected sides. We should think about adding this links for representing side effects.
3) When we draw negative feedback, it is usually comprehensible if there is existing gap which directs toward the goal.
4) In many examples we can accept that there is delay when the actual state is perceived. For this situation it could be important if we include the causal loop diagram for the actual value and the perceived value.
5) In many causal loop diagrams there is no difference between long and short result or process. And this is not so right, because you should make difference between these two states.
6) If you think that the links between two elements are hard to say in a simple way, you should use more simple intermediate elements.
7) For someone who is reading your diagram is necessary to have it in a simple form. There hasn’t be illustrated every detail.
CLDs in practise and their problems
There are many practises of causal loop diagrams in business or workacademy but there are some problems around this diagrams too. We talk about both belove with some examples.
CLD in practise
We can ask how the causal loop diagram is useful in practise. If we develop it and present it carefully, it can be very useful for us.
We can find very successful CLDs in practise. The most popular example are CLDs of population growth (it could be people or animals or both, that doesn’t matter) and resources diagrams. In the population growth diagram we can control how Immigration and the Birth and death rate change over time. There could be a more extensive demographic example with different age groups and other factors (Halbleib, 2014).
But there are other examples of great using of CLDs. CLDs can be useful in causal modelling to understand organizations and businesses. This is trend in the recent years. CLDs are used in business prototyping, where we can model productivity and causes which influence it, e.g. remaining time, schedule pressure, deadline and so on. This causal loop diagram can be seen on picture (Transentis Consulting, 2014).
Other examples of Causal loop diagrams are in medicine, biology or environment. We can demonstrate it on the causal loop diagram of the dynamics of diabetes. The picture and detailed description you can see in (Fonseca i Casas, 2014) or global warming system. There is a possibility to describe cases and effects of fish pond ecosystem by CLDs. PA Consulting Group created CLDs called “Afghanistan Stability / COIN Dynamics“. It is really extensive diagram summarized a snapshot of U.S. military´s plan (PA Consulting Group, 2010).
Problem of CLDs
For many types of examples it is clearer to use a hybrid diagram which contains stock-flow chain. But this could be harder for visual language. There are many problems with notation too. There is not uniform labelling. Sometimes it is used an “s” (means “same”) and “o” (means “opposite”) instead of the + and -. This problem is explained by George Richardson in his paper “Problems with causal loop diagrams” and his conclusion is that it is not good to use “s” and “o” because it is less confusing. (Richardson, 1986) .
Conclusion
In this paper there was desribe causal loop diagram, its creating and using in practise. As we could se CLDs are quite popular diagrams in practise and are widely used. We can use them in business but in academic work too. For their user it is easy to start drawing these diagrams because all you need to draw CLDs is pencil and paper or a whiteboard. There are to many softwares we can use for drawing this type of diagram too, e.g. Vensimo (for free), STELLA (free, but only for 30 days trial) or AnyLogic (free trial) and other software. As it is was said in the chapter "Problems of CLDs", sometimes it can be problem to make causal loop diagram because of various notations. But CLDs can be very help-full still.
Tasks
There are two tasks to practise problem of causal loop diagram. Below there are answers.
Questions
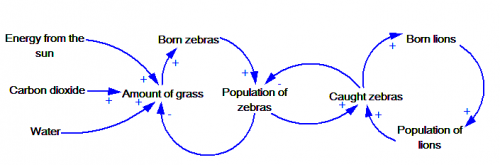
1) Try to illustrated causal loop diagram in the picture dealing with zebras and lions.There are help in the form of preddefined words which should be used in the causal loop diagram.
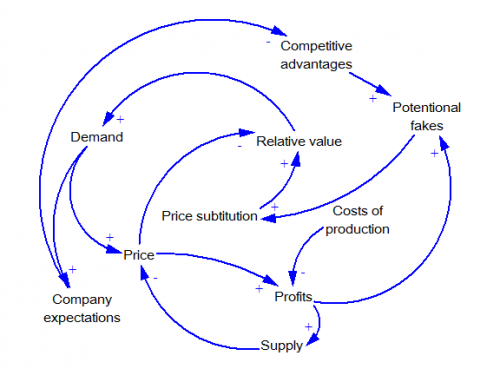
2) Try to draw your own causal loop diagram which is contained from demand, profits, price, market expecations and other things around this thematics.
Answers
Answer for question number 1.
Answer for question number 2 - example how this casual loop diagram could look like.
References
American Creativity Association. 2014. Causal loop diagram. American Creativity Association. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 27 December 2014.] http://www.amcreativityassoc.org/Resources/Documents/CausalLoopDiagrams.pdf.
Fonseca i Casas, Pau. 2014. Formal Language for Computer Simulation:Transdisciplinary Models and Applica\\Ction. Hershey : IGI Global, 2014. 978-1-4666-4370-3.
Halbleib, Harold. 2014. System Models & Simulation. http://www.projectperfect.com.au/. [Online] 7 November 2014. [Cited: 30 December 2014.] http://www.projectperfect.com.au/info_system_models_and_simulation.php.
Haraldsson, Hördur V. 2000. Introduction to Systems and Causal Loop Diagrams. Lunds Universitet. [Online] January 2000. [Cited: 30. December 2014.] http://cmap.crs.org.pl:4444/rid=1244140954250_1167059429_1461/Introduction%20to%20Systems%20and%20Causal%20Loop%20Diagrams.pdf.
Harich, Jack and Bangerter, Philip. 2014. Feedback Loop. http://www.thwink.org/. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 29 December 2014.] http://www.thwink.org/sustain/glossary/FeedbackLoop.htm.
Kirkwood, Craig W. 2013. System behaviour and causal loop diagram. Arizona State University. [Online] 12 January 2013. [Cited: 28 December 2014.] http://www.public.asu.edu/~kirkwood/sysdyn/SDIntro/ch-1.pdf.
Mind Tools Ltd. 2014. Systems Diagrams - Understanding How Factors Affect One Another. http://www.mindtools.com/. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 29 December 2014.] http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMC_04.htm.
Osgood, Nathaniel. 2004. Problem Diagnosis & Introduction to Project Dynamics. http://ocw.mit.edu/index.htm. [Online] 13 April 2004. [Cited: 28 December 2014.] http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/civil-and-environmental-engineering/1-040-project-management-spring-2004/lecture-notes/l16diagnsprjctrl.pdf.
PA Consulting Group. 2010. Afganistan Dynamic Planning. MSNBC media. [Online] 2010. [Cited: 28 December 2014.http://msnbcmedia.msn.com/i/MSNBC/Components/Photo/_new/Afghanistan_Dynamic_Planning.pdf..
Richardson, George P. 1986. Problems with causal-loop diagrams. System thinking. [Online] 1986. [Cited: 29 December 2014.] http://www.systems-thinking.org/intst/d-3312.pdf.
Transentis Consulting. 2014. Causal Loop Diagrams. Business prototyping blog. [Online] 2014. [Cited: 30 December 2014.] http://www.business-prototyping.com/step-by-step-tutorials/. ]